This standard is for products that are intended to enhance the appearance and feel of the skin and hair and provide other personal care and hygiene functions and are left on the body. This includes lotions, moisturizers, oils, powders, creams, sun block, insect repellent, antiperspirant, and deodorant used for adults, babies, children, and professional-use.
GREEN SEAL®
Green Seal is a nonprofit organization whose mission is to use science-based programs to empower consumers, purchasers, and companies to create a more sustainable world. Green Seal sets leadership standards that aim to reduce, to the extent technologically and economically feasible, the environmental, health, and social impacts throughout the lifecycle of products, services, and companies. The standards may be used for conformity assessment, purchaser specifications, and public education.
Green Seal offers certification of products, services, and companies in conformance with its standards. For additional information on Green Seal and contact information, visit greenseal.org.
FOREWORD
Edition. Edition 1.3 was issued on June 23, 2022. It replaces Edition 1.2 from April 8, 2020. Corrections and/or clarifications to this edition were last made on April 29, 2025. Information on changes made to this standard can be found on Green Seal’s website.1Library of Standards Documents, www.greenseal.org/green-seal-standards/library#section20
General. The final issued standard was developed in an open and transparent process with stakeholder input that included producers, users, and general interests.
The requirements in the standard are based on an assessment of the environmental, health, or social impacts associated with the products, services, or organizations covered in the scope of the standard. These requirements are subject to revision, and generally cover aspects above and beyond regulatory compliance. This standard neither modifies nor supersedes laws and regulations. Any conformity assessment to this standard requires compliance with all applicable laws and regulations for the manufacturing and marketing of the products.
Provisions for safety have not been included in this standard, since they are supervised by regulatory agencies. Adequate safeguards for personnel and property should be employed for all stages of production, and for all tests that involve safety considerations.
Products, services, or organizations that are substantially similar to those covered by this standard in terms of function and life cycle considerations may be evaluated against the intent of the requirements of this standard, accounting for relevant differences between the intended scope of the Standard and the actual product, service, or organization to be evaluated.
This standard may not anticipate a feature of the product that may significantly, and undesirably, increase its impact on the environment, health, or society. In such a situation, Green Seal will ordinarily amend a standard to account for the unanticipated environmental, health, or societal impacts.
Normative references (e.g., other standards) in this standard intend to refer to the most recent edition of the normative reference. Test methods may be required for product evaluation. Unless explicitly stated that a specified method is the only acceptable one, the intent of the standard is that an equivalent test method may be accepted at Green Seal’s sole discretion.
Certification to this standard shall be awarded only by Green Seal, or, with Green Seal’s explicit written permission, by a third-party certification program conducting on-site audits.
Disclaimer of Liability. Green Seal, as the developer of this standard, shall not incur any obligations or liability for any loss or damages, including, without limitation, indirect, consequential, special, or incidental damages, arising out of or in connection with the interpretation or adoption of, reliance upon, or any other use of this Standard by any party. Green Seal makes no express or implied warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose, nor any other express or implied warranty with respect to this Standard.
ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
- ACGIH. American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists
- ANSI. American National Standards Institute
- AOEC. Association of Occupational and Environmental Clinics
- BCF. Bioconcentration Factor
- BOD. Biochemical oxygen demand, also known as Biological Oxygen Demand
- BTU. British thermal unit
- CFC. Chlorofluorocarbon
- CFR. Code of Federal Regulations
- CO2. Carbon dioxide
- DFG. German Deustche Forschungsgemeinschaft
- EPA. United States Environmental Protection Agency
- FD&C. Food, Drug, and Cosmetic
- FDA. The United States Food and Drug Administration
- GHS. Globally Harmonized System for the Classification and Labeling of Chemicals
- INCI. International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients
- ISO. International Organization for Standardization
- LLNA. Local Lymph Node Assay
- LOAEL. Lowest-Observed Adverse Effect Level
- MAK. Maximum Allowable Concentrations
- NOAEL. No-Observed Adverse Effect Level
- NSF. NSF International
- OECD. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development
- OPPTS. Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances
- OTC. Over The Counter
- PPM. Parts per million
- SPF. Sun Protection Factor
- ThOD. Theoretical oxygen demand
- TLV. Threshold Limit Value
- USDA. United States Department of Agriculture
- UVA. Ultraviolet A rays/radiation
- UVB. Ultraviolet B rays/radiation
- VOC. Volatile Organic Compound
1.0 SCOPE
This standard establishes environmental, health, and social requirements for products that are intended to enhance the appearance, cleanliness, health/well-being, and feel of the body and hair and may provide other personal care and hygiene functions. These products are left on the body and hair and include, but are not limited to: lotions, hair spray, hair styling products, sunscreen, nail polish, insect repellant, makeup, antiperspirant, and deodorant. The products are intended for use by adults, babies, and children for personal use or for institutional and professional use. See Appendix 1 for an example list of products included in this standard.
This standard excludes fragrance products (e.g., perfumes, colognes, body sprays), tattoo products, hair dye and hair permanent or relaxer products, oral hygiene products (e.g., mouthwash, toothpaste), or products intended to be rinsed off (e.g., soap, shampoo)2Personal care products that are rinsed off are covered under the Green Seal Standard for Soaps, Cleansers, and Shower Products, GS-44..
Words and phrases described in the standard that appear in italics have a corresponding definition located in the definition section of the standard, Annex A.
2.0 SAFER CHEMICALS
2.1 Safer Ingredients
2.1.1 Aquatic Biodegradability. Each of the individual organic compounds at 0.01% or more in the product as rinsed-off shall exhibit ready biodegradability in accordance with the OECD definition, expect for polymers, chelating agents, and colorants. Biodegradability shall be measured according to any of the following methods: ISO 7827, 9439, 10707, 10708, 9408, 14593; OECD Methods 301A – F; or OECD 310. Specifically, within a 28-day test, the organic compounds shall meet one of the following criteria within 10 days of the time when biodegradation first reaches 10%:
- Removal of Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) > 70%
- Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) > 60%
- BOD, as % of Theoretical Oxygen Demand (ThOD) > 60%
- CO2 evolution, as % of theoretical CO2 > 60%
Testing is not required when sufficient information exists. Per OECD guidance the 10-day window requirement does not apply to structurally-related surfactant homologues. For organic compounds at 0.01% or more in the product as used that do not exhibit ready biodegradability in these tests the manufacturer may demonstrate biodegradability in sewage treatment plants using the Coupled Units Test found in OECD 303A by demonstrating DOC removal > 90%.
An exception shall be made for organic compounds that do not exhibit ready biodegradability, if the compound has low aquatic toxicity (acute LC50 ≥ 100 mg/L for algae, daphnia, and/or fish) and exhibits inherent biodegradability per ISO test methods 9887 or 9888 or OECD 302A-C.
2.1.2 Bioaccumulating Compounds. The product as rinsed-off shall not contain any components at 0.01% or more that bioaccumulate or that are known to form degradation products that bioaccumulate. A chemical is considered to bioaccumulate when it has a bioconcentration factor (BCF) ≥ 500 (or log Kow ≥4). The preferred source of data is from OECD TG 305 (for BCF). If the chemical meets the requirement for biodegradability, 2.1.1 herein, it may be considered to not bioaccumulate.
2.1.3 Biocides. The use of biocides for purposes other than preservation of the product is not allowed. Documentation and testing results shall be provided to demonstrate the dosage necessary to preserve the product. An exception shall be made for deodorant and antiperspirant products such that they are permitted to include biocides for purposes other than preservation.
2.1.4 Carcinogens and Reproductive Toxins. The undiluted product shall not contain any components that are carcinogens or reproductive toxins. The product shall not contain any components known to produce or release carcinogens or reproductive toxins. An exception shall be made for titanium dioxide. An exception shall also be made for essential vitamins and minerals, which shall not exceed the lowest tolerable upper limit in the product.
2.1.5 Colorants. Colorants are prohibited. An exception shall be made for makeup, nail polish, and sunless tanning products.
2.1.6 Components That Cause Asthma. The undiluted product shall not contain any components that have been identified as asthmagens. An exception shall be made for zinc oxide.
2.1.7 Endocrine Disruptors. The undiluted product shall not contain any components that are on the EPA List of Chemicals for Tier 1 Screening that have been shown to disrupt hormones (e.g., have estrogen- or androgen-mediated effects), tested according to the EPA Series 890 – Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program Test Guidelines.
2.1.8 Formula Disclosure for Certification. For certification to this standard, all of the formula components shall be disclosed to the certifying body including the chemical name, the Chemical Abstracts Service registry number, and the levels (% by weight) of each component in the formula.
2.1.9 Fragrances. All fragrance components shall have been produced and handled following the code of practice of the International Fragrance Association (IFRA).
2.1.10 Makeup and Nail Polish Lead Contamination Limits. The lead content of undiluted makeup and nail polish products shall not exceed 0.05 parts per million (ppm).
2.1.11 Mutagens and Neurotoxins/Systemic Toxins. The undiluted product shall not contain any components that have been identified as mutagens or neurotoxins/systemic toxins. An exception shall be made for essential vitamins and minerals, which shall not exceed the lowest tolerable upper limit in the product.
2.1.12 Nanoscale Components. The use of nanoscale components shall only be permitted when the European Commission Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (formerly known as the Scientific Committee for Consumer Products) provides an opinion that allows for their safe use for products included in the scope of this standard. If the opinion allows for the safe use of nanoscale components, then the product label shall indicate that the component is “nanoscale” or “nanoparticle” on the ingredient line.
2.1.13 Ozone Depleting Compounds. The undiluted product shall not contain any components that are ozone-depleting compounds.
2.1.14 Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). The undiluted product shall not contain any components that are Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS).
2.1.15 Prohibited Components. The undiluted product shall not contain any of the following components:
- 2-butoxyethanol
- Alkylphenol ethoxylates
- Benzophenone and its derivatives
- Bisphenol A
- Butylated hydroxytoluene
- Ethoxylated chemicals
- Ethylene-diamine-tetra-acetic acid or any of its salts
- Formaldehyde donors
- Halogenated organic solvents
- Hazardous air pollutants
- Heavy metals including, lead, hexavalent chromium, or selenium both in the elemental form or compounds
- Methyldibromo glutaronitrile
- Mercury-containing compounds
- Mineral oils
- Monoethanolamine, Diethanolamine, and Triethanolamine alone or in compounds
- Nitrilotriacetic acid
- Nitro-musks
- Optical brighteners
- Parabens
- Paraffin wax
- Petrolatum
- Phthalates
- Polycyclic musks
- Toxic Release Inventory Persistent, Bioaccumulative, and Toxic Chemicals
- Triclosan
2.1.16 Respiratory Sensitization. The undiluted product shall not contain any components that have been identified as respiratory sensitizers.
2.1.17 Skin Absorption. The undiluted product shall not contain components present at greater than or equal to 1% in the product, that are listed on the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) threshold limit value (TLV) carrying a skin notation, or substances that are listed on the German Deustche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) maximum allowable concentrations (MAK) list with a skin absorption H notation. Further, the product shall not contain components at 0.01% or more in the undiluted product that sum to 1% in the formula that are listed on ACGIH or DFG with the same target organ.
2.1.18 Skin and Eye Corrosion and Irritation.
2.1.18.1 Skin and Eye Corrosion. The undiluted product shall not cause skin corrosion or cause serious eye damage. For purposes of demonstrating compliance with this requirement, data may be evaluated for each of the product’s components at 0.01% or more in the undiluted product. If the components at 0.01% or more in the undiluted product are not shown to cause skin corrosion or serious eye damage at the concentrations used, then the product will not be considered to cause skin corrosion or serious eye damage, unless the product is required to be labeled as such. Further, a product is considered to cause skin corrosion or to cause serious eye damage if it has a pH of 2 or less or a pH of 11.5 or greater, unless data prove otherwise.
2.1.18.2 Skin Irritation. The undiluted product shall not cause skin irritation. For purposes of demonstrating compliance with this requirement, data may be evaluated for each of the product’s components at 5% or more in the undiluted product. If the components at 5% or more in the undiluted product are not shown to cause skin irritation at the concentrations used, then the product will not be considered to cause skin irritation.
2.1.19 Skin Sensitization. The undiluted product shall not be a skin sensitizer. For purposes of demonstrating compliance with this requirement, data may be evaluated for each of the product’s components at 0.01% or more in the undiluted product. If the components at 0.01% or more in the undiluted product are not shown to be skin sensitizers at the concentrations used, then the product will not be considered to be a skin sensitizer.
2.2 Safer Products
2.2.1 Acute Toxicity. The undiluted product shall not be toxic to humans. A product is considered toxic if any of the following criteria apply3Products meeting the requirements in 2.2.1 will not fall into hazard categories 1 through 5 for acute oral and dermal toxicity and will not fall into hazard categories 1 through 4 for acute inhalation toxicity under the Globally Harmonized System for the Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) when the whole product is evaluated using the weighted average approach described.:
- Oral lethal dose (LD50 ) < 5,000 mg/kg
- Inhalation lethal concentration (LC50) < 200 mg/L at 1 hr (dusts, mists and vapours)
- Inhalation lethal concentration (LC50) < 20,000 ppmV at 1 hr (gases)
- Dermal lethal dose (LD50) < 2,000 mg/kg
For purposes of demonstrating compliance with this requirement, existing acute toxicity data for each of the product’s components at 0.01% or more in the undiluted product will be used. This data is used to calculate a weighted average that assumes that the toxicity of the individual components is additive. The toxicity values are adjusted by the weight of the components in the product and summed using the following formula:
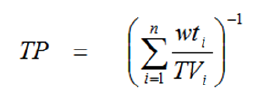
Where,
TP = toxicity of the product
wti = the weight fraction of the component
TV = the toxicity value for each component (LD50)
n = number of components
Inhalation toxicity shall be determined from all components at 0.01% or more in the undiluted product, when the component has a vapor pressure greater than 1 mm Hg at 1 atm pressure and 20°C.
2.2.2 Eutrophication. The undiluted product shall not contain phosphorus at more than 0.2% by weight.
2.2.3 Toxicity to Aquatic Life. The product as rinsed-off shall not be toxic to aquatic life. A product is considered not toxic to aquatic life if4Products meeting the above will not fall into in categories 1, 2 or 3 for acute (short-term) hazards to the aquatic environment (H400, 401, and 402) under the GHS.:
- Acute LC50 for fish, daphnia, and/or algae ≥100 mg/L
For purposes of demonstrating compliance with this requirement, data for each of the product’s components at 0.01% or more in the product as rinsed-off can be used to calculate a weighted average (as in section 2.2.1). The preferred sources of data come from the following appropriate protocols in International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 7346-2 for fish, OEDC Test Guidance (TG) 203 for fish, OECD TG 202 for daphnia, or OECD TG 201 for algae.
2.2.4 Chronic Aquatic Toxicity. The product as rinsed-off shall not contain any components at 0.01% or more that have chronic aquatic toxicity. The preferred sources of data are from OECD TG 210 for fish, OECD TG 211 for daphnia, or OECD TG 201 for algae. If adequate chronic aquatic toxicity data is not available, the guidance in GHS shall be followed for classification of the chemical.
2.2.5 Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Content.
2.2.5.1 Total VOC Content. The undiluted product shall contain no more than current VOC regulatory limits of the Air Resources Board for the State of California (CARB) or the following VOC content (% by weight), whichever is more stringent:
| Products | VOC Content (% by weight) |
| Astringent/toner | 35% |
| Hair spray, hair shine, and insect repellent | 55% |
| Hair styling products not sold in pump spray packaging | 2% |
| Hair styling products sold in pump spray packaging | 5% |
| Nail polish | 75% |
| All other products | 1% |
The VOC content shall be determined in one of the following ways:
- By summing the percent by weight contribution from all organic components of the product that have a vapor pressure of greater than 0.1 mm mercury at 1 atm pressure and 20º C.
- According to the California Air Resources Board Method 310 (or equivalent), modified to include all fragrances and all organic components5Evaluation of total VOCs in this standard includes all fragrances and all organic compounds present in the product at 0.01% or more. Evaluation of total VOCs under Method 310 exempts fragrances and all organic compounds present below 0.1%..
2.2.5.2 High and Medium Volatility Organic Compound Content. Antiperspirant and deodorant undiluted products shall meet the CARB Regulation for Reducing Volatile Organic Compound Emissions from Antiperspirants and Deodorants, specifically those regulations pertaining to high and medium VOCs and including the exceptions provided in the regulations.
2.2.6 Sunscreen.
2.2.6.1 Enhanced Sensitivity to UV. Sunscreen products shall not contain components that are known to enhance the skin’s sensitivity to UV radiation including, but not limited to, alpha hydroxy acids and retinoids.
2.2.6.2 Product Form. Sunscreen products shall not be sold as powders or in pump spray packages.
2.2.7 Insect Repellent. Insect repellent shall not be combined into sunscreen products (or vice versa).
2.2.8 Animal Testing. Animal testing of the product or its components in order to meet the provisions in the standard is prohibited.
To avoid new animal testing, existing data from previous testing will be accepted as evidence of meeting a criterion, preferably tests following the methods accepted by the Interagency Coordinating Committee on the Validation of Alternative Methods or the European Centre for the Validation of Alternative Methods, unless indicated otherwise. In addition, non-animal (in-vitro) test results, modeling data, data from structural analogs, and other lines of evidence may be accepted, provided that the methods are peer-reviewed, applicable, and the manufacturer provides rationale for the particular method.
3.0 RESPONSIBLE SOURCING
3.1 Disposable Wipes.
Products may contain disposable towelettes or other disposable wiping materials if they are made from 100% renewable materials including, but not limited to cellulosic materials, and meet the state-of-the-art amount of recovered material content.
4.0 LOW-IMPACT MANUFACTURING
4.1 Social Responsibility.
Documentation shall be provided that product production meets the following social responsibility requirements:
4.1.1 Freedom of Association and Collective Bargaining. Workers shall have the right to join or form trade unions of their own choosing and their right to bargain collectively shall be recognized and respected. An exception shall be made for inmate workers.
4.1.2 Freedom of Labor. There shall not be forced or bonded labor or use of child labor.
4.1.3 Freedom from Discrimination. There shall not be discrimination in terms of race, color, sex, religion, age, disability, gender, marital status, sexual orientation, union membership, political opinion, national extraction or social origin such that it affects the opportunity or treatment in employment and there shall be no support or tolerance of corporal punishment, physical or verbal coercion, sexual or other harassment, intimidation or exploitation.
4.1.4 Occupational Health and Safety. A safe and hygienic workplace environment shall be provided with access to potable water. Adequate steps shall be taken to minimize the hazards of the workplace and workers shall receive health and safety training to prevent accidents and injury.
4.1.5 Conditions of Employment. Workers shall work under fair conditions of employment. Wages, working hours and overtime shall meet at a minimum the national legal or industry benchmark standard and regular employment shall be provided.
5.0 SUSTAINABLE PACKAGING
5.1 Packaging Materials
5.1.1 Source Reduction in Packaging. The primary and secondary packaging shall be at least one of the following:
- Source-reduced package
- Recyclable and contain at least 25% post-consumer material or demonstrate that efforts were made to use the maximum available post-consumer material in the package
- Packaging with an effective take-back program
- Contain at least 50% post-consumer material
- An alternative approach may be acceptable that has been independently proven to have a similar life cycle benefit as at least two of the above approaches for a substantial majority of communities
5.1.2 Concentrated Product Packaging. Concentrates are prohibited from being packaged in ready-to-use forms, including but not limited to pump spray packages.
5.1.3 Aerosol Packaging. Aerosol packages are prohibited.
5.1.4 Pump Spray Packaging. Pump spray packages are prohibited for antiperspirants, deodorants, sunless tanning products, and sunscreen products.
Exemption: Antiperspirants and deodorants that are not formulated with aluminum compounds or titanium dioxide6CAS Number 13463-67-7 may be sold in pump spray packages.
5.2 Packaging Label
5.2.1 Use Labeling. The product shall be accompanied by detailed instructions for proper use to maximize product performance and minimize waste.
5.2.2 Resin Identification Code. If plastic, the packaging shall be marked with the appropriate Society of the Plastics Industry symbol to identify the type of plastic for recycling. If the symbol is in a conspicuous location, the appropriate qualification of recyclability is required such as “this product may not be recyclable in your area, see if accepted by your local program” or “only a few communities accept this package for recycling, check with your local program.”
5.3 Restricted Substances
5.3.1 Heavy Metal Restrictions. Heavy metals, including lead, mercury, cadmium, and hexavalent chromium, shall not be intentionally introduced in packaging and applicators. Further, the sum of the concentration levels of these metals present shall not exceed 100 ppm by weight (0.01%); an exception is allowed for refillable packages or packages/applicators that would not exceed this maximum level but for the addition of recovered materials. Further, intentional introduction does not include the use of one of the metals as a processing aid or intermediate to impart certain chemical or physical changes during manufacturing, where the incidental retention of a residual of that metal in the final packaging/applicator or packaging/applicator component is not desired or deliberate, if the final packaging/applicator or packaging/applicator component complies with the incidental concentration restrictions of 100 ppm.
5.3.2 Other Restrictions. Phthalates, bisphenol A, and chlorinated packaging and applicator material are prohibited from being intentionally introduced; an exception is allowed for packages and applicators that would not have these added compounds but for the addition of recovered material.
6.0 VERIFIED PERFORMANCE AND CLAIMS
6.1 Product Performance.
The product shall demonstrate satisfactory performance for the primary product characteristics (see Appendix 2 for examples) following the Guidelines for Performance Testing in Annex B.
6.1.1 Antiperspirant. The antiperspirant product shall demonstrate at least a 20% reduction in sweat according to the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Guidelines for Effectiveness Testing of Over-the-Counter (OTC) Antiperspirant Drug Products and meet 2.1 herein for additional primary product characteristics.
6.1.2 Insect Repellent. The product shall include active components that are registered with the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for use as an insect repellent on skin or clothing. Note that EPA may specify use levels or packaging types for registered components. Alternatively, minimum risk pesticide-based products shall demonstrate that they meet the guidance in the EPA Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances (OPPTS) 810.3700 Insect Repellents for Human Skin and Outdoor Premise.
6.1.3 Sunscreen.
6.1.3.1 Sun Protection Factor (SPF). Sunscreen products shall achieve an SPF rating of 15 or higher tested according to 21 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) 352 for sunscreens.
6.1.3.2 Broad Spectrum. Sunscreen products shall be tested according to the European Commission Recommendation of 22 September 2006 on the Efficacy of Sunscreen Products and the Claims Made Relating Thereto for ultraviolet A (UVA) protection achieving at least 1/3 of the SPF and at least 370 nm for the critical wavelength.
6.1.3.3 Photostability. Sunscreen products shall be tested for photostability using an objective, scientifically-validated method conducted under controlled and reproducible conditions to measure sun protection from UVA and UVB radiation exposure that is representative of a sunny, mid-summer day at noon at sea level and up to 55º North latitude. The sun protection of the product after at least 120 minutes of radiation exposure shall be at least 80% of the sun protection before radiation exposure.
6.2 Product Label
6.2.1 Ingredient Line. The product label on each package shall list the product ingredients using the naming convention of the International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) in order of predominance. Ingredients in concentrations of less than 1% may be listed in any order after those in concentrations of more than 1%. The general term ‘fragrance’ may be used for fragrance components.
6.2.1.1 Nanoscale Component Labeling. Products that contain nanoscale components shall indicate that the component is “nanoscale” or “nanoparticle” on the ingredient line.
6.2.1.2 Consumer Communication. The product ingredient line (6.2.1 herein) shall be made available to consumers in an easily accessible means besides the label on each package, such as the company website.
6.2.2 Precautionary Statements. Products that contain components that are known to enhance the skin’s sensitivity to UV radiation including, but not limited to, alpha hydroxy acids and retinoids shall include a labeling statement about the increased risk of sun damage possible when exposed to sun. Further, statements about protecting the skin from the sun shall be included on the label such as, but not limited to: staying out the sun as much as possible, wearing protective clothing, and using sunscreen appropriately, such as the language in the FDA Guidance: Labeling for Cosmetics Containing Alpha Hydroxy Acids.
6.2.3 Small Packages. Packages containing less than one-eighth fluid ounce (or equivalent for other product forms) is exempt from labeling for each package the information included in the following provisions herein: 6.2.1 Ingredient Line; 6.2.2 Precautionary Statements. However, all of the information from these provisions shall be available to the consumer through other means (e.g., package, website).
6.2.4 Disposal Labeling. The label shall include proper disposal instructions including clear package recycling instructions, if applicable.
6.2.5 Efficacy Labeling.
6.2.5.1 Antiperspirant Efficacy Labeling. The product shall meet the requirements for a claim made on antiperspirant effectiveness (e.g., extra-effective, enhanced duration) according to the FDA Guidelines for Effectiveness Testing of OTC Antiperspirant Drug Products.
6.2.5.2 Insect Repellent. The label for insect repellent products shall indicate the protection time as determined by the EPA OPPTS 810.3700 Insect Repellents for Human Skin and Outdoor Premise.
6.2.5.3 Sunscreen Efficacy Labeling. The label for sunscreen products is permitted to claim “broad spectrum” since it meets appropriate performance requirements (6.1.3.2 herein).
6.2.6 Claims and Transparency
6.2.6.1 Antimicrobial Claims. The product shall make no antimicrobial, disinfecting, antiseptic, or sanitizing product claims. An exception shall be made for deodorant and antiperspirant products.
6.2.6.2 Organic Claims. Organic claims shall only be based on certified-organic component content and shall be supported with documentation that they meet the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) National Organic Program, programs determined to be equivalent by or have recognition agreements with the USDA National Organic Program or meet the NSF International (NSF)/American National Standards Institute (ANSI) 305 standard.
6.2.6.3 Natural and Biobased Claims. Only the following natural and biobased, or related, claims are allowed when the product meets the following criteria:
“100 percent Natural”, “All Natural”, “100 percent Biobased”, or “All Biobased” shall only contain natural or biobased components, respectively, excluding water, and with no petroleum, silicone, or synthetic components.
- “Natural” or “Biobased” products shall contain 95% natural, naturally-derived, or biobased components, respectively, excluding water.
- Claims on specific product components being “natural” or “biobased” may be permitted if it is a natural or biobased component.
6.2.6.4 Fragrance and Allergen Labeling. The label for each package shall declare, separate from the ingredient line, if a fragrance has been added or if no fragrance has been added and shall also indicate any allergen components in the product (e.g., Contains allergen [allergen’s INCI name]).
7.0 TRADEMARK USE REQUIREMENTS
7.1 Trademark Use.
Any use of the Green Seal® Certification Mark or Green Seal name, e.g., on the product, product label, packaging, secondary documents, or promotional materials, must be in accordance with Green Seal’s Trademark Use Guidelines.7
7.2 Misleading Claims.
Green Seal trademarks shall not be used in conjunction with any modifying terms, phrases, or graphic images that might mislead consumers as to the extent or nature of the certification.
Annex A – Definitions (Normative)
Note: the defined terms are italicized throughout the standard.
Active Component. A component in a product that provides, or partly provides, the primary product characteristic.
Allergen. Allergenic substances listed by the European Commission Directive76/768/EEC, 27 July 1976 on the Approximation of the Laws of the Member States relating to Cosmetic Products (also known as the Cosmetic Directive) in Annex III and those listed by the FDA (including food allergens Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act of 2004 (Public Law 108-282, Title II).
Alpha Hydroxy Acid. Substances that are organic carboxylic compounds substituted with a hydroxyl group on the adjacent carbon. This includes, but is not limited to, glycolic acid, lactic acid, malic acid, citric acid, and tartaric acid. These may be natural or synthetic.
Antimicrobial. Substances that are intended to kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms including antiseptic, disinfectant, and sanitizer substances.
Antiperspirant. A product that is applied topically to the body that reduces the production of perspiration at that site. These products are regulated as drugs by the FDA. These products may also function as deodorants.
Antiseptic. Substances that are intended to prevent or arrest the growth of microorganisms.
Applicator. An item included in the packaging that is intended to be used to apply the product on the body or hair. It is typically, but not necessarily, a separate item in the package. This includes, but is not limited to, brushes, sponges, and swabs. This does not include tubes or bottles that can be used to apply the product (e.g., lip products). While the applicator may be part of the primary package (e.g., nail polish, mascara), for the purposes of this standard it is not considered primary packaging. An exception is for pencil-like products (e.g., eye liner), the material in direct contact with the product is considered the applicator and any material used around this is considered either primary or secondary packaging.
Asthma. Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways that impairs breathing. Asthma affects children and adults, may be intermittent or persistent, and is further classified as mild, moderate, or severe. The chronic inflammation associated with variable airflow obstruction commonly causes difficulty breathing, coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and/or chest pain. Symptoms may resolve completely between active episodes. Symptoms may occur during exposure, immediately after exposure, or up to 24 hours later in a “late phase,” frequently interrupting sleep.
Asthmagen. A substance designated as an asthma causing agent by the Association of Occupational and Environmental Clinics (AOEC), which after review by AOEC have met the AOEC sensitization criteria.
Astringent/Toner. A product applied to the skin for the purpose of cleaning or tightening pores and are not rinsed off of the skin. This category does not include any hand, face, or body cleaner or soap products that are rinsed off of the body.
Biobased. The content of a product that is from biological products or renewable materials, forestry, or agricultural materials (including plant, animal, and marine materials).
Biocide. Substances intended to destroy, deter, render harmless, prevent the action of, or otherwise exert a controlling effect on any harmful organism by chemical or biological means. These are considered antimicrobial, antiseptic, disinfectant, or sanitizing agents.
Carcinogen. A substance listed as a known, probable, reasonably anticipated, or possible human carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (Groups 1, 2A, and 2B), National Toxicology Program (Groups 1 and 2), EPA Integrated Risk Information System (weight-of-evidence classifications A, B1, B2, C, carcinogenic, known/likely human carcinogen, likely to be carcinogenic to humans, and suggestive evidence of carcinogenicity or carcinogen potential), by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (as carcinogens under 29 CFR 1910.1003(a)(1)), or under the GHS (hazard categories 1 (H350, may cause cancer) and 2 (H351, suspected of causing cancer)).
Certified-Organic Component. A component certified as organic (by meeting the USDA organic standards) by a USDA-accredited certifying agent, or by programs determined to be equivalent or have recognition agreements with the USDA National Organic Program (NOP).
Child Labor. The minimum age for admission to employment as outlined in the Convention Concerning Minimum Age for Admission to Employment such as, but limited to, a minimum age not less than 15 or the age of completion of compulsory schooling in the country of production, whichever is older, and for work that is likely to jeopardize health, safety, and morals of young persons the minimum age not less than 18.
Chronic Aquatic Toxicity. Substances that cause long-lasting adverse effects to aquatic organisms and classified in hazard categories 1 through 4 for long-term hazards to the aquatic environment (H410 through H413) under the GHS.
Colorant. A product component that is included primarily to deliver color to the product or user.
Component. A deliberate addition to the product added at any level or a contaminant that was not deliberately added but is known to be present above 0.01% (100 parts per million), by weight, in the product. Naturally occurring elements and chlorinated organics, which may be present as a result of chlorination of the water supply, are not considered components if the concentrations are below the applicable maximum contaminant levels in the National Primary Drinking Water Standards found in 40 CFR Part 141.
Concentrate. A product, as sold, that must be diluted with water prior to its intended use.
Deodorant. A product that is applied topically to the body to reduce the body odor caused by the bacterial breakdown of perspiration.
Disinfectant. An antimicrobial agent intended to and capable of destroying pathogenic and potentially pathogenic microorganisms on inanimate surfaces.
Drug. The Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic (FD&C) Act defines drugs, in part, by their intended use, as “articles intended for use in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease” and “articles (other than food) intended to affect the structure or any function of the body of man or other animals” [FD&C Act, sec. 201(g)(1)].
Fragrance. An additive, often (but not limited to) a multi-component additive, used for the purpose of imparting or neutralizing a scent in the product.
Fragrance Product. Products with the primary function of imparting and diffusing a fragrant odor, such as, but not limited to, perfumes, colognes, and body sprays. These products are typically highly volatile. For the purposes of this standard, skin care, deodorant, and antiperspirant products are not considered fragrance products.
Globally Harmonized System for the Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. The GHS established hazard classes and means for classifying substances; substance classification based on these hazard classes has been listed by the European Chemicals Agency and the ex-European Chemicals Bureau, or is disclosed on a Safety Data Sheet.
Good Manufacturing Practices. Incorporation of quality practices and procedures, such as those included in the FDA’s Inspection Operations Manual, to minimize the risk of adulterated or misbranded products.
Hair Shine Product. A product designed for the primary purpose of creating a shine when applied to the hair.
Hair Styling Product. A product that is designed or labeled for the application to wet, damp, or dry hair to aid in defining, shaping, lifting, styling, and sculpting of the hair. This also includes leave-in volumizers, detanglers, and conditioners that make styling claims.
Hair Spray. A product that is applied to styled hair, and is designed or labeled to provide sufficient rigidity, to hold, retain, and finish the style of the hair for a period of time.
Halogenated Organic Solvent. An organic solvent containing halogens, including fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine.
Hazardous Air Pollutant. A substance listed by the EPA in the Clean Air Act Section 112(b) (1) as a hazardous air pollutant.
High and Medium Volatility Organic Compound. An organic compound that exerts a vapor pressure greater than 2 mm mercury at 1 atm pressure and 20ºC.
Insect Repellent. A product that is intended to be applied to the skin, hair, or clothing to help reduce exposure to insects or prevent insect bites.
Intentional Introduction. The act of deliberately utilizing a material in the formation of a package or packaging component where its continued presence is desired in the final package or packaging component to provide a specific characteristic, appearance, or quality.
Lotion. Products that are left on the body to enhance the appearance or feel of the body including, but not limited to: creams, moisturizers, powders, serums, oils, and sprays for use on the face and neck, body, hand, cuticle, foot, and hair.
Makeup. Products that are applied topically and are used to temporarily color and enhance the appearance of facial and body features. Lip balm may be considered makeup if it has colorant components intended to temporarily color or enhance the appearance of the lips.
Minimum Risk Pesticide. A special class of pesticides (including insect repellents) that are not subject to federal registration requirements through the EPA because they meet specific requirements under section 25(b) of the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), including, but not limited to, that the components, both active and inert, are demonstrably safe for the intended use.
Mutagen. A substance designated as known to induce, be regarded as if it induces, or which causes concern for humans owing to the possibility that it may induce heritable mutations in the germ cells of humans and thus meets the criteria for hazard categories 1 and 2 (H340 and 341) under the GHS.
Nail Polish. Products that are applied to and form a film on the nail. They are used to color the nails, harden the nails, protect the nails, or nail treatments to address specific nail conditions, such as peeling or brittleness. These products may include top coats and base coats and may also be referred to as lacquers or enamels.
Nanoscale Component. Insoluble or biopersistent components that are intentionally manufactured to be roughly 1 to 100 nanometers in size in at least one dimension externally or within the internal structure (i.e., primary particle). This size typically enables novel applications that a larger-sized version of the component could not achieve.
Natural Component. A component that comes from materials found in nature including mineral, forestry, agricultural, or biological materials such as, but not limited to, animal products produced by the animal but not part of the animal; they do not contain petroleum or petroleum-derived compounds; they do not contain transgenic hybrid organisms (inserted deoxyribonucleic acid that originated in a different species); they have been processed without irradiation; and they are not chemically altered.
Naturally-Derived Component. A component that is partially chemically altered without petroleum components and have been minimally processed such that they not be altered to such an extent that they are substantially less biodegradable or more toxic (examples of potentially acceptable processes are included in Appendix 3).
Neurotoxin/Systemic Toxin. A substance designated as producing a specific target organ toxicity arising from either single exposure or repeated exposure and thus meets the criteria for hazard categories 1 or 2 (H370, H371, H372, H373) under the GHS.
Optical Brightener. An additive designed to enhance the appearance of colors and whiteness in materials by absorbing ultraviolet radiation and emitting blue radiation. These compounds are also known as fluorescent whitening agents.
Organic Compound. Any member of a large class of chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon, with the exception of carbides, carbonates, cyanides, diamond and graphite.
Ozone-Depleting Compound. A compound with an ozone-depletion potential greater than 0.01 (Chlorofluorocarbon – CFC 11=1) according to the EPA list of Class I and Class II Ozone-Depleting Substances or any substances or mixtures falling into hazard category 1 (H420) under the GHS.
Package/Packaging. This includes the applicator, primary package, and any secondary package used for the product. It does not include case or shipping material.
Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). A class of fluorinated organic chemicals containing at least one fully fluorinated carbon atom.
Photostability. The ability of a product to retain its initial level of sun protection efficacy after ultraviolet A and B (UVA and UVB) radiation exposure.
Post-Consumer Material. Material that would otherwise be destined for solid waste disposal, having completed its intended end-use and product life cycle. Post-consumer material does not include materials and by-products generated from, and commonly reused within, an original manufacturing and fabrication process.
Primary Package. A package that is the material physically containing and typically coming into contact with the product. This does not include the cap or lid of a bottle. Product applicators are not considered part of the primary package.
Primary Product Characteristic. The main function for which the product category is intended for use. See Appendix 2 for an example list of primary product characteristics of products included in this standard.
Product As Rinsed-Off. The dilution of the product for removal from the body at a rate of 5 ml per liter of water, or equivalent measure for another product form (e.g., solid, foam).
Protection Time. The time from application of the insect repellent to the time until the first bite or until the repellent no longer reduces bites by 95%, as determined by the EPA Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances (OPPTS) 810.3700 Insect repellents for human skin and outdoor premise. This is the period of time a repellent is expected to remain effective. For ticks and chiggers, this refers to the period between the time of application of the repellent to time of a tick or chigger crawling onto human skin.
Pump Spray. A package that dispenses the product through a nozzle after a pump was triggered. It does not require a pressurized propellant to dispense the product.
Recyclable. The package can be collected in a substantial majority of communities, separated or recovered from the solid waste stream and used again, or reused in the manufacture or assembly of another package or product through an established recycling program.
Reproductive Toxin. A substance listed as a reproductive toxin (including developmental, female, and male toxins) by the State of California under the Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act of 1986 (California Code of Regulations, Title 22, Division 2, Subdivision 1, Chapter 3, Sections 1200, et. Seq., also known as Proposition 65) or a substance designated as hazard category 1 (H360), known or presumed reproductive toxicant, category 2 (H361), suspected human reproductive toxicant, or having adverse effects on or via lactation (H362), under the GHS.
Respiratory Sensitizer. A substance designated as leading to hypersensitivity of the airways following inhalation of the substance from human evidence or appropriate animal test and thus meets the hazard criteria for category 1 (H334) under the GHS.
Retinoid. Vitamin A (all-trans-retinol; retinol), its metabolites, analogues, and derivatives. This includes, but is not limited to, retinyl palmitate, retinol, retinaldehyde, and retinoic acid. These may be natural or synthetic.
Sanitizer. A product intended to reduce the level of microorganisms present to acceptable levels established by federal or provincial health authorities.
Secondary Packaging. Packaging used to contain primary package/s and typically used for merchandizing. This does not include case or shipping packaging or the primary package, cap, or lid.
Serious Eye Damage. The production of tissue damage in the eye, or serious physical decay of vision, following application of a test substance to the anterior surface of the eye, which is not fully reversible within 21 days of application. Substances classified as Category 1 for Serious Eye Damage/Eye Irritation (H318) under the GHS are also considered to cause serious eye damage.
Skin Corrosion. The production of irreversible damage to the skin; namely, visible necrosis through the epidermis and into the dermis, following the application of a test substance for up to 4 hours. Corrosive reactions are typified by ulcers, bleeding, bloody scabs, and, by the end of observation at 14 days, by discoloration due to blanching of the skin, complete areas of alopecia, and scars. Substances designated as Category 1A, 1B, or 1C for Skin Corrosion/Irritation (H314) under the GHS are also considered to cause skin corrosion.
Skin Irritation/Irritant. The production of reversible damage to the skin following the application of a test substance for up to 4 hours. Identified under hazard categories 2 or 3 for skin irritation/mild skin irritation (H315 and H316) by the GHS.
Skin Sensitizer. A substance that will lead to an allergic response following skin contact. Identified under hazard category 1 for skin sensitization (H317) under the GHS.
Source-Reduced Package. A package that has at least 20% less material (by weight) compared to containers commonly used for that product type.
Sunscreen. Products that intend to protect the body from UV radiation by absorbing, scattering, or reflecting radiation.
Sunless Tanning Product. Products applied to the skin to produce an effect similar in appearance to a traditional suntan without exposure to UV radiation. These products are also known as self-tanning products.
Synthetic Component. Components that are created artificially rather than naturally or from natural components. For the purposes of this standard, naturally-derived components are not considered synthetic components.
Take-Back Program. A program sponsored by the original product manufacturer that has been demonstrated to receive at least 50% of sold containers for recycling or reuse.
Tolerable Upper Limit. The highest level of daily nutrient intake that is likely to pose no risk of adverse health effects to almost all individuals in the general population, as established by the Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine, National Academies.
Toxic Release Inventory Persistent, Bioaccumulative, and Toxic Chemicals. The chemicals listed by the EPA on the Toxic Release Inventory as Persistent, Bioaccumulative, and Toxic (PBT) Chemicals.
Undiluted Product. The most concentrated form of the product produced by the manufacturer for distribution outside its facility.
Ultraviolet A. A type of solar radiation within the region of the electromagnetic spectrum from 320 to 400 nanometers (nm) that penetrate deep within the skin causing damage.
Ultraviolet B. A type of solar radiation within the region of the electromagnetic spectrum from 290 to 320 nm that cause redness and burning of the skin.
Annex B – Guidelines for Performance Testing (Normative)
The product shall demonstrate satisfactory performance, which includes at a minimum the primary product characteristics (see Appendix 2 for examples). Testing may be completed through one of the following means:
1. A quality test using an objective, scientifically-validated method conducted under controlled and reproducible conditions. This may be conducted by the manufacturer or an external laboratory that has ISO 9001 registration or equivalent quality control verification.
2. A comparative test demonstrating performance equivalent to or better than a nationally recognized or market-leading product in its product category. This may be conducted by the manufacturer or an external laboratory that has ISO 9001 registration or equivalent quality control verification.
3. A consumer-based product comparison test. The test shall have a minimum of ten (10) panelists that may be internal or external to the organization, but should maintain a neutral position (i.e., chosen at random). The consumers shall be surveyed about the product’s efficacy compared to a market-leading product. A summary of conclusions and a description of how panelists are chosen shall be submitted. The following are some example questions that could be used:
- How well does the product perform in comparison with the market-leading product with regard to primary product characteristics?
- How does the condition of the hair and/or skin feel after use in comparison with the market-leading product?
Appendix 1 – Scope (Informative)
Examples of products included in or excluded from the scope of GS-50:
- Aftershave
- Astringent/toner
- Cleaning wipes that don’t require rinsing after use
- Cuticle cream, lotion, and oil
- Deodorant and antiperspirant
- Hair shine products
- Hair spray
- Hair styling products (e.g., balm, gel, mousse)
- Insect repellents
- Leave-on hair conditioner
- Lip products
- Makeup and bronzers (e.g., foundation, concealer, bronzer, mascara, eyeliner, eye shadow, blush)
- Massage oil
- Nail polish
- Skin care products (e.g., lotions, moisturizers, creams, oils, serums)
- Sunless tanning products
- Sunscreen
- Artificial nails, glues, and removers
- Artificial lashes
- Bubble bath and bath salts (included in GS-44)
- Exfoliant products (if rinsed off, included in GS-44)
- Feminine deodorant
- Fragrance Products/perfume and body spray
- Hair dye, color, and bleach
- Hair relaxants
- Hand sanitizers
- Nail polish remover
- Oral care products (toothpaste)
- Products intended to be edible
- Shaving cream, gel, and foam (included in GS-44)
- Soap and cleansers (included in GS- 44)
- Tattoos
Appendix 2 – Primary Product Characteristics (Informative)
Examples of primary product characteristics:
- Antiperspirant: Meet FDA guidelines for standard effectiveness of sweat reduction, malodor reduction
- Deodorant: Malodor reduction
- Hair Spray: Quick drying, hold power, removability (brushing, shampooing)
- Hair Styling Products: Styling power, removability (brushing, shampooing)
- Insect Repellent: Meet the EPA guidelines for Insect Repellents for Human Skin and Outdoor Premise.
- Lotions: Hydration, smoothness/softness
- Makeup: Last, removability
- Nail Polish: Quick drying, nail appearance, durability
- Sunless Tanning Products: Suntan appearance
- Sunscreen: SPF, UVA protection, broad UV protection, photostability
Refer to the European Cosmetics Association, COLIPA “Guidelines for the Evaluation of the Efficacy of Cosmetic Products,” May 2008 for information on test design and data evaluation.
Appendix 3 – Processing Methods of Naturally-Derived Components (Informative)
Examples of Potentially Acceptable Processing Methods of Naturally-Derived Components (which must also meet all the requirements in the standard):
- Esterification, Etherification, and Transesterification (to produce esters and ethers like polyglycerols)
- Glucosidation (to produce glucosides)
- Hydrogenation (of fats and oils)
- Hydrolysis and Hydrogenolysis (to produce hydrolyzed proteins, glycerin and fatty acids, and fatty alcohols)
- Other Condensation Reactions like Acylation of proteins and Sulfation of fatty alcohols
- Saponafication (to produce soap)